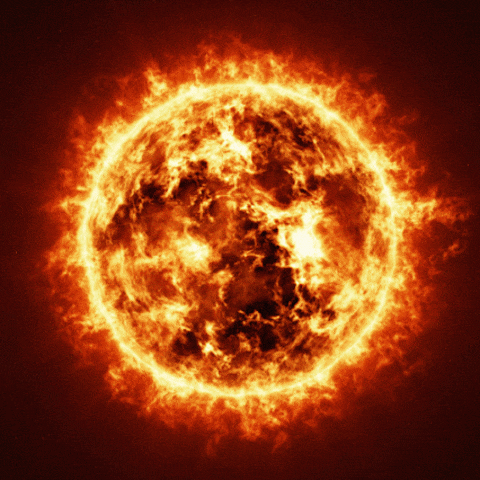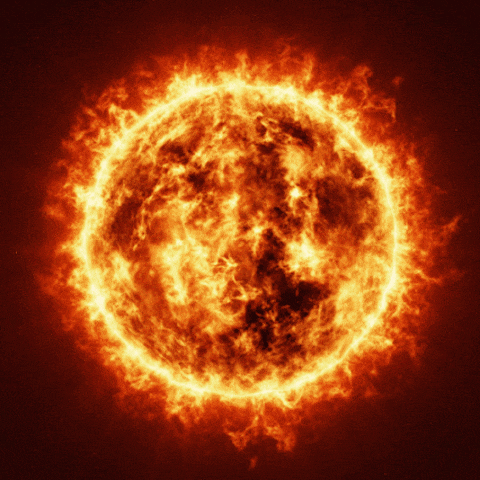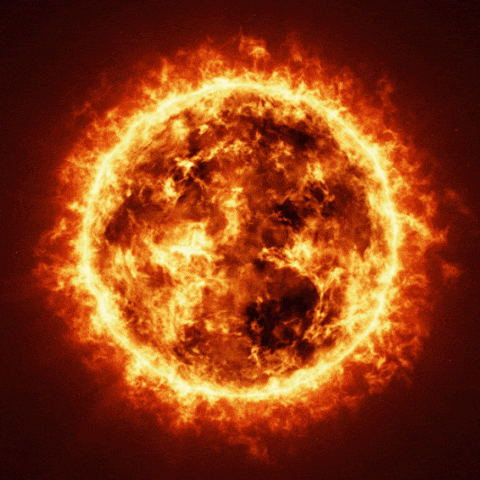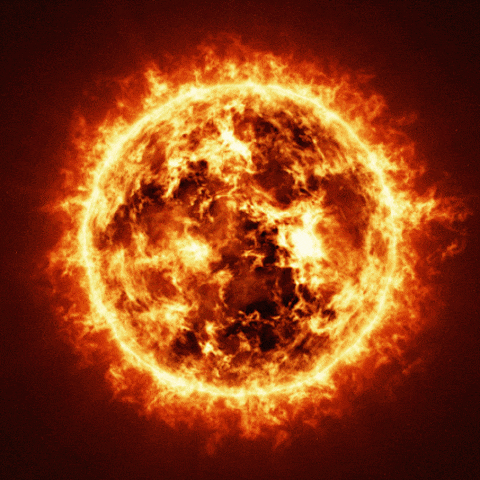
The Sun
features
The sun is the source of life
The Sun is the main source of light, heat and energy on our planet
500 seconds
That’s how long it takes solar photons to reach the Earth. That’s 150 million kilometers!
Moonlight
The Moon doesn’t shine, it only reflects solar photons
Solar mass
99.8% of the mass of the Solar System is contained within the Sun. All the other planets together make up only 0.2%
January
Our planet is closest to the Sun in January
Milky Way
The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way
Jeremy England
If you start with a random clump of atoms, and if you shine light on it for long enough, it should not be surprising that you get a plant
The Sun is our energy source
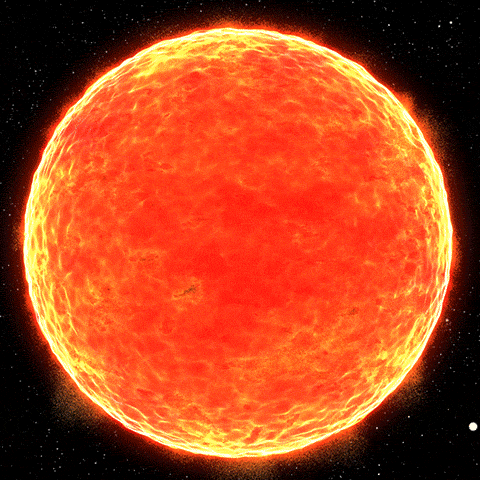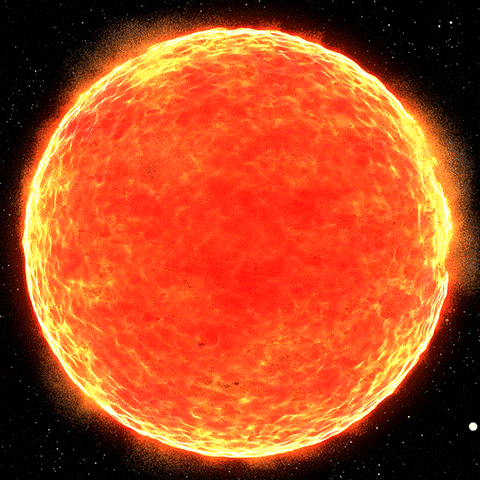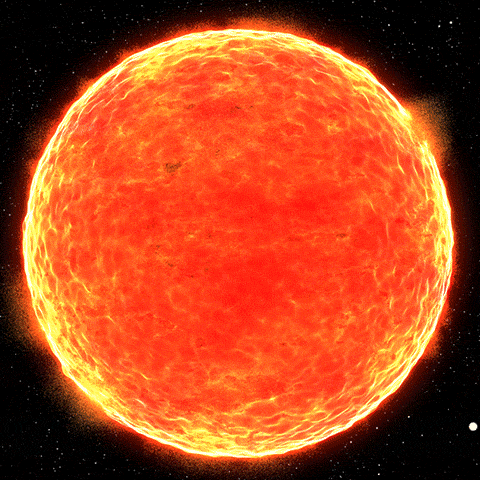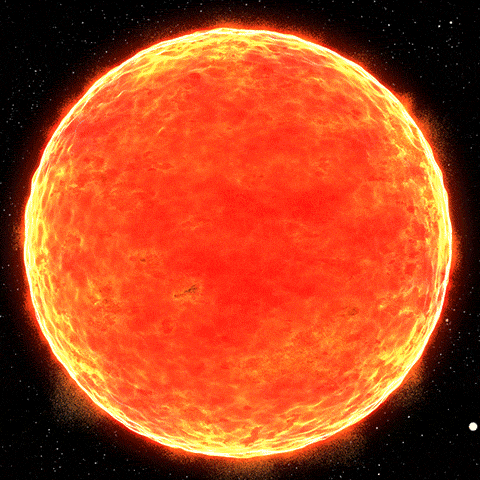
Imagine a huge bonfire whose radiation power exceeds our imagination – this is the Sun, a star in the Milky Way galaxy. The Sun is the primary and constant source of energy for the Earth. Currently, the Sun is located on the inner edge of the Orion Arm of our galaxy, between the Perseus Arm and the Sagittarius Arm
Hydrogen energy
The Sun is primarily composed of hydrogen (73%) and helium (25%). It radiates power at an astonishing rate of 3.8×10^26 (26 zeros!) Watts per second. This immense radiation is due to thermonuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, producing huge amounts of photons in the process. Essentially, the Sun is a massive nuclear reactor, transforming hydrogen into helium and emitting vast quantities of energy.
Despite appearing yellow from Earth due to atmospheric effects, the Sun’s true color is bright white. It is the only star in our solar system and is currently in the middle of its life cycle, estimated to last about 10 billion years. At 4.5 billion years old, the Sun remains the primary source of light and energy for our planet.

Sun's effect on the Earth
Sunlight sustains life on Earth and determines our climate. Plants use the energy from photons for photosynthesis, which produces oxygen. In the distant past, photosynthesis also contributed to the formation of oil and other fossil fuels by storing energy. Mankind has learned to convert solar energy into electricity. The Sun heats the surface of the Earth, promoting the development of life. The energy of solar photons per square meter of area can reach up to 1 kWatt at the equator at zenith. This is equivalent to the power of an electric kettle! The main source of this energy is photons

Uniqueness of solar radiation
The spectral range of the Sun’s electromagnetic radiation (photon emission) is very wide, spanning from radio waves to X-rays. The maximum intensity of radiation in the visible spectrum occurs in the yellow-green part. However, the strongest radiation that reaches the Earth is invisible to the human eye
Infrared is the strongest
Distribution of Solar Photons by Wavelength Near the Earth’s Surface:
- 9.1% is in the invisible short-wave ultraviolet range (up to 380 nm). Most of the UV spectrum is absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer.
- 44.6% falls within the visible spectrum (380-780 nm).
- 46.3% lies in the infrared and radio range (over 780 nm).

Solar magnetic fields
Spots appear periodically on the Sun due to magnetic fields. As a result, solar flares (solar explosions) occur. These flares emit a stream of accelerated particles, producing a huge number of additional photons and altering the Sun’s electromagnetic radiation levels. There are also sources of radiation in the radio band. Coronal mass ejections, solar wind perturbations, and variations in galactic cosmic ray fluxes are all due to strong magnetic fields. This is known as solar activity. The appearance of sunspots is not predictable and is considered spontaneous and random

Solar events
When coronal mass ejections (CMEs) from the Sun reach the Earth, magnetic storms begin. The Earth then receives a much larger number of photons above the infrared spectrum, along with streams of high-energy particles (helium-hydrogen plasma). These particles, as they lose energy, emit photons as well. This results in the occurrence of auroras, also known as the northern lights.
Learn more about these and other solar events in this section

Global warming
There is a perspective that global warming in the second half of the 20th century is linked to an increase in solar activity. During the maximum of the eleven-year solar cycle, the most powerful magnetic fields, reaching several thousand gauss, are observed in sunspot groups.
This viewpoint suggests that the heightened solar activity during this period contributed to changes in the Earth’s climate. Sunspot groups, which are associated with strong magnetic fields, can influence the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth. Consequently, variations in solar activity may have a significant impact on global temperatures and climate patterns

The importance of solar photons
his site was created to draw attention to the effect of photon energy on humans. After all, trillions of photons pass through, are reflected by, or are absorbed by a person every second!
The radiation of the Sun in the ultraviolet range is particularly important for humans. Under the action of ultraviolet light, the vital vitamin D is formed. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to a serious disease called rickets. Due to the lack of ultraviolet rays, the normal intake of calcium can be disrupted, and the permeability of body tissues increases

question - answer
Do you have a Question?
Everything is good in moderation. Excessive solar radiation can certainly be harmful. However, the Sun is the source of life, and a lack of its light is also detrimental. Balance is important!
This is the outer shell of our star. It is the hottest visible part of the Sun, with a unique radiation spectrum. It can be seen during a total solar eclipse
In its calm state, hydrogen’s wavelength of 121.6 nm is the most intense. However, it does not reach the Earth, as it is almost completely absorbed by the atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere absorbs most of the Sun’s X-ray and ultraviolet radiation. However, for radio waves and microwaves, whose sources are magnetic spots, the atmosphere of our planet is practically transparent. Radiation at wavelengths of 1-50 cm fully reaches the Earth, and the atmosphere does not affect it
The Earth revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit. The closest distance to our luminary is in January (147 million kilometers), called perihelion. The farthest distance is in July (152 million kilometers), called aphelion
Yes, the magnetic field consists of photons. Additionally, the invisible connection between the poles of a metal magnet is due to the exchange of photons at the speed of light
what else is interesting?
More interesting and useful information